Water pollution: types, consequences, and solutions
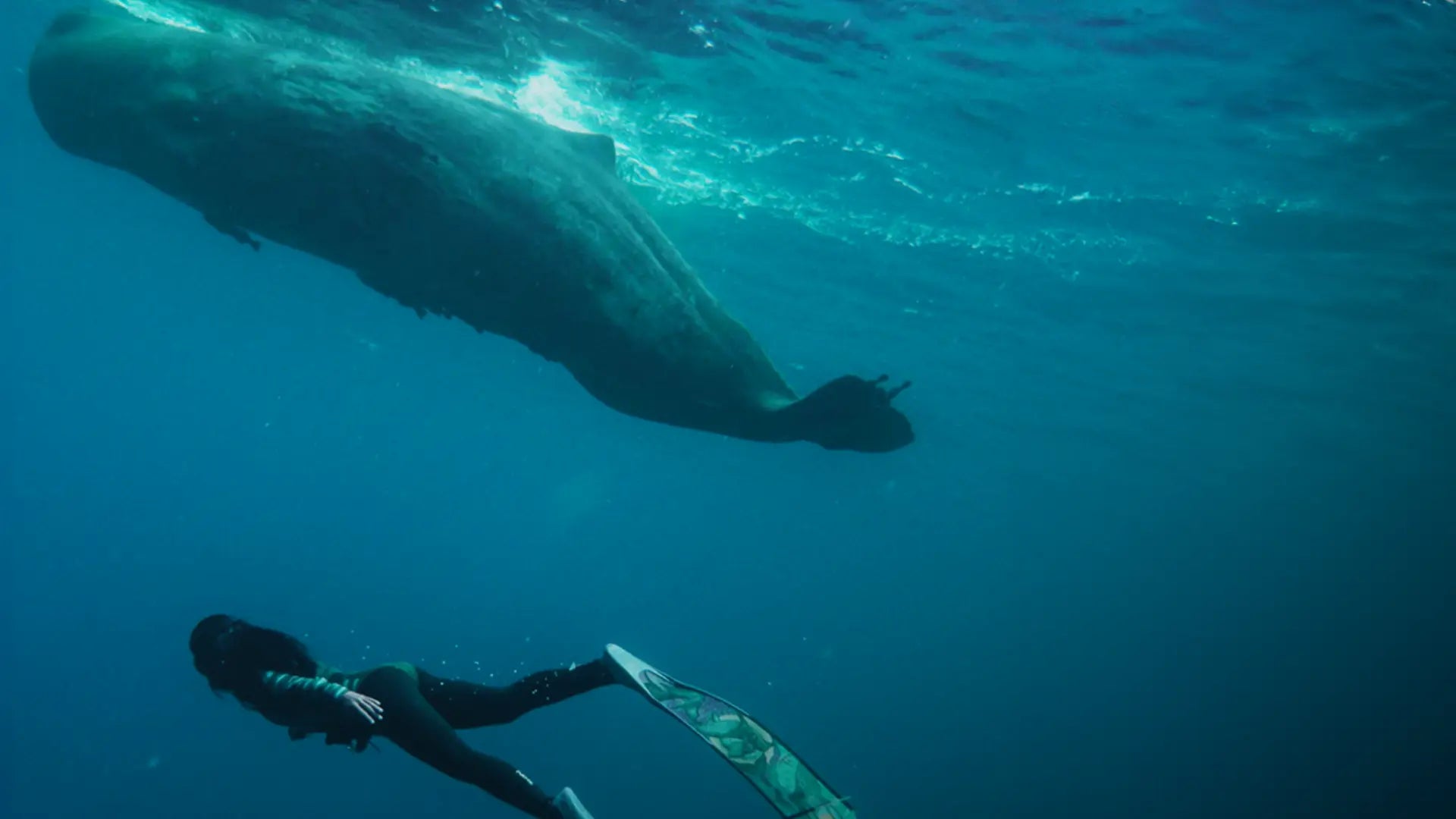
Pollution – the scourge of the 21st century! Water pollution is a critical global problem that threatens ecosystems and human health. Pollution of waters, from rivers to lakes, leads to severe consequences, including contamination of drinking water and damage to aquatic organisms.
Pollution of the world's oceans is particularly alarming, as over 80% of the waste in the seas comes from land-based sources, leading to the death of countless ocean species. Pollution of the world's oceans not only disrupts the balance of marine ecosystems but also creates long-term risks for biodiversity and the resilience of our environment.
Sources of Water Pollution:
Ocean pollution extends far beyond trash and plastic. Major sources of water pollution include:
-
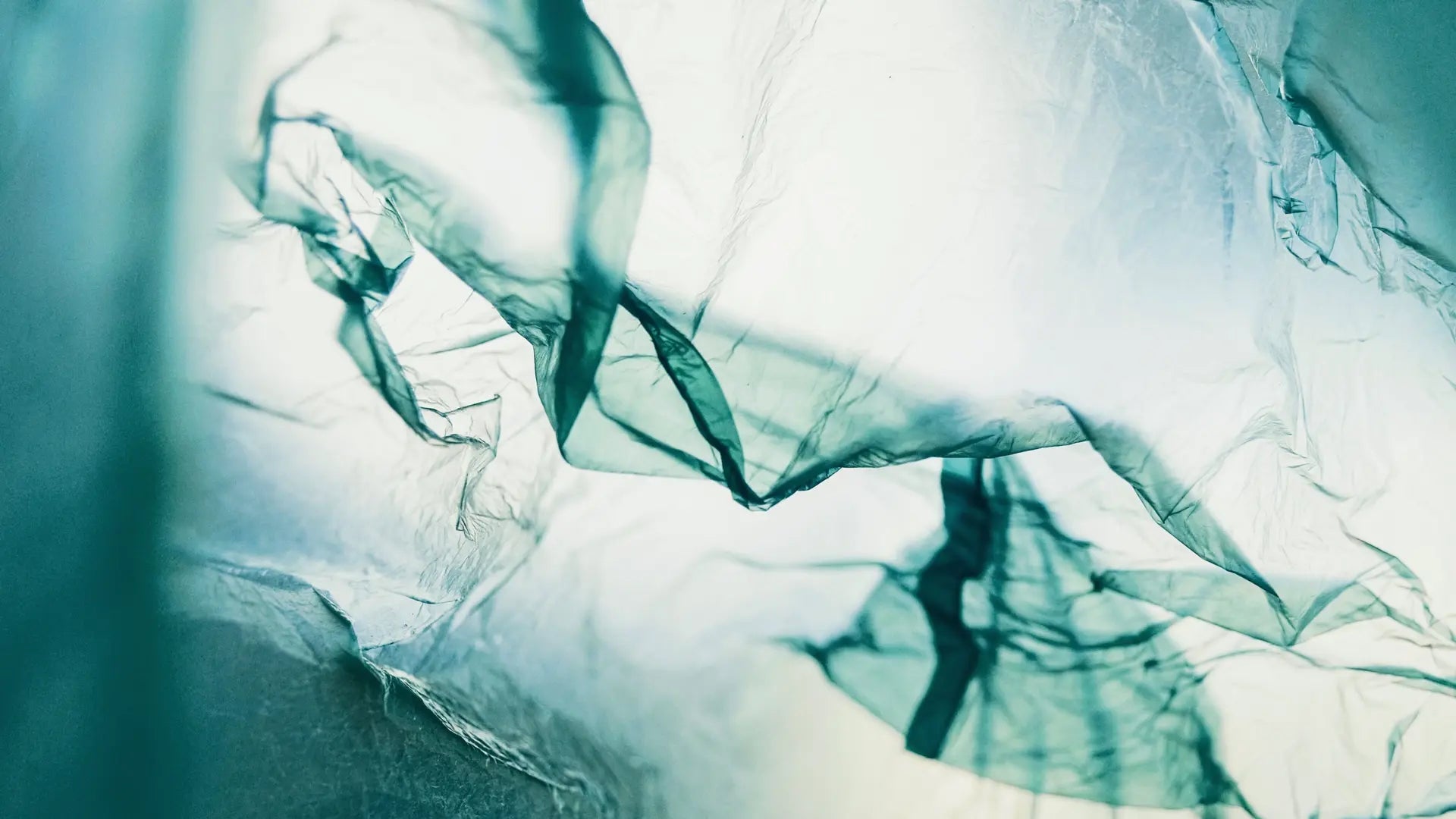
Chemical pollutants and plastic
Chemical pollution of water mainly comes from industry and household activities. These pollutants enter the oceans through rivers and runoff, leading to toxic environments and harm to the marine ecosystem. Plastic waste can cause entanglement of various animals or problems with accidental ingestion. Prevention requires stricter regulations, waste control, and public awareness campaigns.
-
Water pollution with oil
It occurs in accidents involving oil tankers, drilling platforms, or pipelines. When oil enters the ocean, it spreads over the water surface, damaging marine life, covering the shores, and disrupting ecosystems. The impact is long-lasting, with some effects continuing for decades. Preventing spills requires strict safety measures, equipment maintenance, and rapid response strategies.
-
Wastewater
It comes from untreated or inadequately treated wastewater discharged into the oceans. Harmful bacteria, viruses, and excess nutrients are produced, leading to oxygen depletion and dead zones. The impact includes algal blooms and destruction of marine habitats. Addressing this issue requires better wastewater treatment infrastructure and stricter control.
-
Agricultural runoff
Agricultural runoff, rich in fertilizers and pesticides, flows into the oceans from farms, causing chemical and nutrient pollution. This leads to algal blooms that deplete oxygen levels and create dead zones, harming marine life. Reducing agricultural runoff requires sustainable farming practices, no fertilizers, and better land management to control erosion.
-
Heavy metal pollution
Heavy metals, such as mercury and lead, enter the oceans from mining production, industrial activities, and improper disposal of electronic waste. They accumulate in marine organisms, leading to toxic effects and entry into the food chain. The impact includes poisoning of marine life and humans. Reducing heavy metal pollution involves stricter environmental regulations and initiatives for recycling.
-
Noise pollution
It is mainly caused by shipping, industrial activities, and military sonars. Intense noise disrupts communication, navigation, and reproduction of marine animals, especially for species like whales and dolphins. This disturbance can lead to stress, disorientation, and even death. Combating noise pollution involves implementing quieter ship technologies, regulating industrial noise, and creating protected marine areas.
Each type of pollution carries its own set of harmful consequences, each of which represents a serious threat to marine life and ecosystems. These pollutants disrupt natural processes, damage habitats, and contribute to the ongoing degradation of our oceans.
Consequences of Water Pollution
Ocean pollution threatens both the environment and human health. Pollutants lead to the degradation of marine ecosystems, threatening the survival of countless species. Heavy metals, chemicals, and plastic pollution disrupt the natural balance, destroy or damage habitats, and reduce biodiversity. This loss of marine life can have catastrophic effects, disrupting entire ecosystems and benefits for nature.
Marine pollution directly affects public health. The presence of dangerous pathogens and toxins can lead to the spread of waterborne diseases such as cholera and dysentery. Long-term exposure to polluted water can also cause chronic health problems, including cancer and neurological disorders, due to the accumulation of harmful substances like mercury and lead.
The most dangerous for human health are the toxins entering the food chain. Marine organisms, from plankton to fish, can absorb and concentrate pollutants, which then reach humans. This bioaccumulation poses serious risks to human health, as the consumption of contaminated marine species can lead to poisoning and other health complications.
Water pollution also contributes to the risk of eutrophication, a process where excessive nutrients, often from agricultural runoff, lead to the overgrowth of algae. When the algae die and decompose, oxygen levels in the water are depleted, creating dead zones where marine life cannot survive. These dead zones further worsen biodiversity loss and disrupt the balance of marine ecosystems.
Pollution of the world's oceans is a dangerous and widespread problem. It leads to the destruction of marine ecosystems, creates significant risks to public health, and causes the entry of toxins into the food chain. Solving this problem requires urgent and coordinated efforts to reduce pollution at its sources and to restore the health of our water bodies.
Measures for the Protection of the World Ocean
Water conservation requires collective action and everyone can play a crucial role. One of the most effective methods is recycling. Proper sorting and recycling of waste helps reduce the amount of plastic and other harmful materials that end up in the oceans. Campaigns like this one by "Krilixir" are fundamental, as they promote recycling initiatives and encourage people to participate in reducing ocean pollution.
In addition to recycling, choosing eco-friendly household products is another way to protect the oceans. Many everyday cleaning products contain chemicals that harm marine life when they enter waterways. By choosing eco-friendly alternatives, people can reduce the amount of harmful substances that reach the oceans.
Supporting foundations and non-governmental organizations dedicated to ocean conservation is another effective way to contribute. Organizations like Krilixir, Aker BioMarine and Surfrider Foundation work tirelessly to clean beaches, advocate for policies that protect marine life, and educate the public about the importance of preserving our oceans.
Volunteering is another powerful tool in the fight against ocean pollution. Regular clean-ups of coastal strips and conservation programs rely on volunteers who remove trash from beaches and educate others about the importance of protecting our oceans. Participation here not only helps clean the environment but also raises awareness.
Protecting the world's oceans is a responsibility we all share. By actively participating in recycling, supporting environmental organizations, choosing eco-friendly products, and volunteering, we can all play a role in preserving our oceans for generations to come. Recycling campaigns, such as this one by Krilixir, are leading the way, and the participation of each individual is crucial to making a lasting difference.
FAQ:
1. What are the main water pollutants?
The main pollutants of the world's oceans can be grouped into several types: chemical pollutants and plastics; water pollution with oil; wastewater; agricultural runoff; pollution with heavy metals and noise pollution.
2. Why is water pollution dangerous?
Water pollution can lead to severe consequences for both the environment and the marine ecosystem. In turn, this can have a negative impact on human health and the overall existence of our planet.
3. How to keep the water clean?
To protect water cleanliness, resources should be invested in recycling programs, control, additional regulations, encouragement of volunteering and donations, awareness and prevention campaigns, as well as commitment from major industries, manufacturers, and companies.